X3 Fixed Prices Rules (X3 EN)
This data is stored centrally via the PIM.
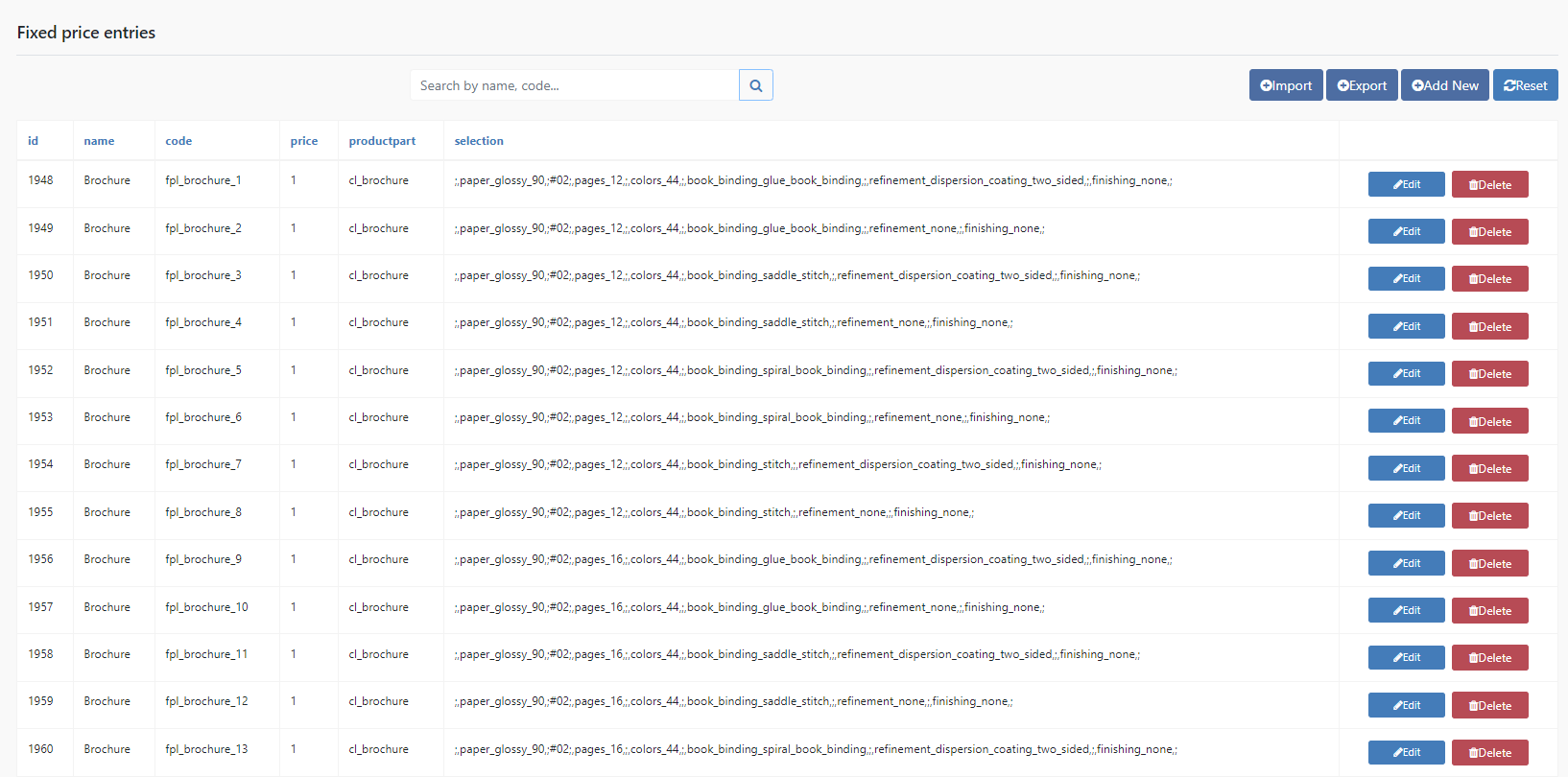
Import/Export
The import/export is done via .csv file. Please note that our .csv must be opened and separated by a semicolon and the character set must be set to UTF-8. If you use Excel, it is best to open the file via the import function.
Alternatively, free alternatives like LibreOffice can help. Here a selection is displayed at the beginning, how the file should be opened.
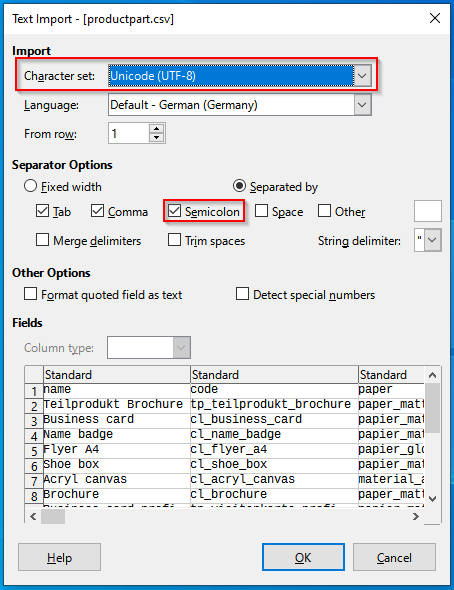
Codes are then used within the .csv. Fill in the individual fields and import the list again afterward. IMPORTANT: Deleting via import is not possible. If you want to import e.g. a list with only 5 new product parts, this is possible without any risk.

Add New
Create a new Fixed Prices Rule List in the Datacenter.
Reset
Resets the current filter.
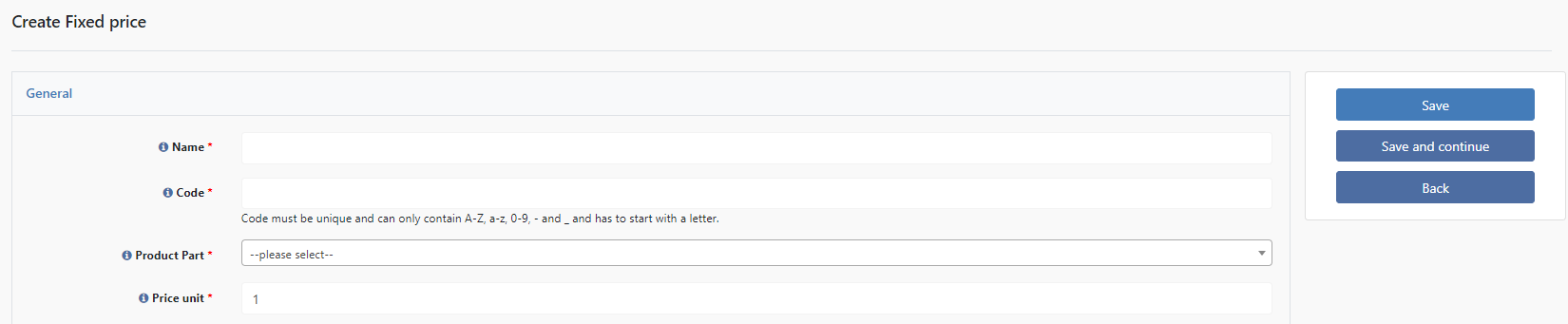
General
Name
Name of the fixed price list. This is not published on the frontend
Code
Code of the fixed price list for system-wide referencing.
Product Part
Here you select the Product Part to which the fixed price list applies.
Price unit
The quantity to which the price stored in the price scales refers (e.g. 1 means a price per piece. If 50, it means that the price in the price scale applies to 50 pieces).
Tier Prices
Our Tier prices in the fixed price list interpolate the prices between two quantities.
Here is an arbitrary example:
Actual quantity: 50
Tier Prices:
Quantity | Price |
|---|---|
1 | 7.5 |
10 | 5.5 |
100 | 4.5 |
500 | 3 |
for quantity 50 we consider the pairs "10, 5.5" and "100, 4.5".
QUANTITY X = 50
PRICE A = 5.5 * 10 (price * qty)
PRICE B = 4.5 * 100 (price * qty)
QUANTITY_OF_STEEL A = 10
QUANTITY_STEFFEL B = 100
( ( 450 - 55 ) ÷ ( 100 - 10 ) ) × ( 100 - ( 100 - 50 + 10 ) ) + 55 = 230.5555
The result of the formula gives the price for the current total quantity of 50, this price is divided by the current quantity to get the unit price
So the price used in the calculation, the result of the function "getTierPrice", is 4.61111.
If, on the other hand, you want prices without interpolation then create the scales with intermediate steps. In this case, the above example would be as follows:
Quantity | Price |
|---|---|
1 | 7.5 |
9 | 7.5 |
10 | 5.5 |
99 | 5.5 |
100 | 4.5 |
499 | 4.5 |
500 | 3 |
If you maintain the scales in this way, the formula will not be able to calculate a lower price between two quantities, so the interpolation will be "leveraged" and you will get fixed unit prices.
